Bilge dumping, an often-overlooked environmental problem, poses significant threats to our oceans and marine life.
Bilge dumping refers to the illegal discharge of bilge water – a mixture of water, oil, and other fluids collected in the lowest part of a ship’s hull – into the ocean. This practice, harmful to marine ecosystems, violates international maritime laws aimed at preventing marine pollution.
This article delves deep into the phenomenon of bilge dumping, examining its causes, legal implications, and possible solutions.
Understanding Bilge Dumping
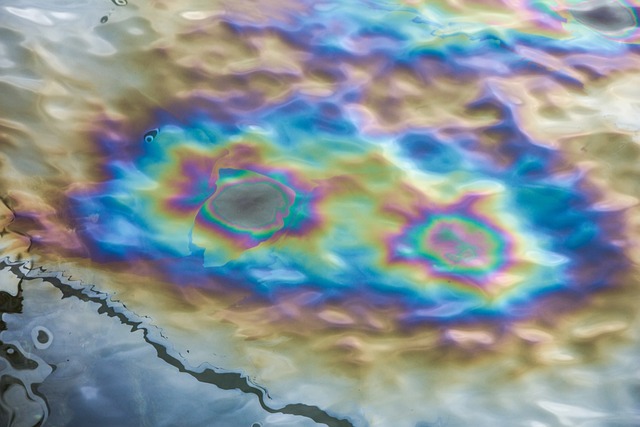
Bilge dumping, a critical environmental issue, involves the disposal of bilge water into the ocean. Bilge water, found at the lowest part of a ship’s hull, is an accumulation of various substances, including water, oil, grease, sludge, chemicals, and other waste products. This mixture results from a range of shipboard operations and daily activities.
The primary concern with bilge water is its potential contamination due to the oil and chemicals it contains. When discharged improperly, this water can cause extensive harm to marine ecosystems. The oil in bilge water, even in small amounts, can spread over large areas of the ocean surface, affecting marine life and bird populations, and impairing the beauty and utility of affected water bodies.
The process of bilge water formation begins with the collection of rainwater or seawater that enters the ship, along with various operational fluids like lubricants and coolants. Over time, this collection becomes a complex mixture, necessitating proper treatment before disposal.
Modern ships are equipped with bilge water separators and treatment systems that help in separating oil and other contaminants from the water, rendering it safe for discharge under specific conditions set by maritime laws.
However, despite technological advancements, the improper handling and illegal discharge of bilge water remain significant challenges. This leads us to the question of why such practices continue to occur in the maritime industry.
Why Bilge Dumping Happens
There are several reasons why bilge dumping occurs, ranging from economic to operational factors:
- Cost and Convenience: Properly treating and disposing of bilge water can be expensive and time-consuming. Some ship operators resort to illegal dumping as a cost-saving measure, bypassing the costs associated with proper disposal.
- Lack of Adequate Facilities: In some cases, especially in older ships, adequate bilge water treatment systems may not be available. This lack of facilities can lead to the improper handling of bilge water.
- Operational Challenges: During long voyages, the capacity to store bilge water may be exceeded, and in the absence of treatment facilities, some operators may choose to dispose of the bilge water illegally to free up space.
- Insufficient Enforcement and Monitoring: The vastness of the oceans and limited monitoring capabilities make it challenging to enforce regulations effectively. Some operators take advantage of these limitations to engage in illegal dumping.
- Lack of Awareness or Training: Crew members may not always be adequately trained or aware of the environmental impact of bilge dumping and the importance of adhering to regulations.
- Pressure to Meet Schedules: The maritime industry is often under tight schedules. The pressure to maintain these schedules can lead to corner-cutting practices, including the illegal disposal of bilge water.
Stopping this requires a multifaceted approach involving stricter enforcement, better training and awareness programs, technological advancements, and a collective commitment from the maritime industry to uphold environmental standards.
Bilge Dumping Effects on Marine Life
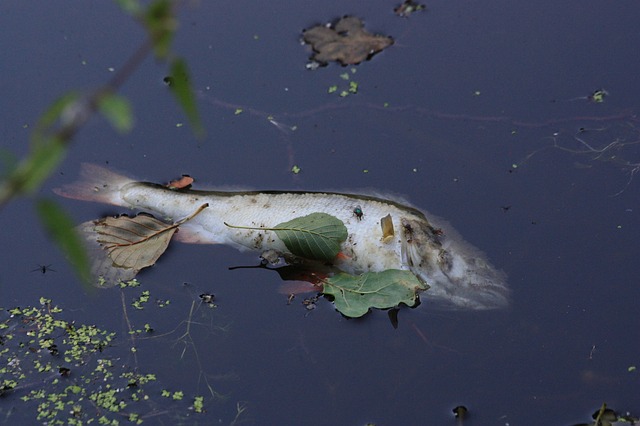

Bilge dumping has profound and detrimental effects on marine life.
The oil and chemicals in bilge water can create a film on the water’s surface, obstructing sunlight and oxygen essential for marine ecosystems. This surface layer can harm photosynthesis in aquatic plants, disrupting the food chain.
Fish and other marine animals may ingest toxic substances from bilge water, leading to health issues, reproductive problems, and mortality. The contamination also affects birds, as oil can impair their feathers’ waterproofing and insulation, leading to hypothermia or drowning.
Furthermore, bilge dumping can degrade coral reefs, vital to biodiversity and ocean health. These reefs, already under stress from climate change and pollution, face an increased risk of bleaching and disease when exposed to bilge water contaminants.
Overall, bilge dumping contributes to the degradation of marine habitats, reduces biodiversity, and poses a significant threat to the health and survival of numerous marine species.
Legal Perspective on Bilge Dumping
The legality of bilge dumping is governed by a complex framework of international laws and agreements, with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) playing a pivotal role.
Key among these legal frameworks is the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, known as MARPOL (Marine Pollution), specifically Annex I, which deals with the prevention of pollution by oil.
- MARPOL Annex I Regulations: These regulations set strict limits on the oil content in bilge water that can be legally discharged into the ocean. Ships are required to use oil-water separators and retain oil residues onboard for disposal at port waste reception facilities.
- Enforcement and Penalties: The enforcement of these regulations falls under the jurisdiction of both the flag states (countries where ships are registered) and port states. Violations can result in hefty fines, vessel detentions, and in severe cases, criminal charges against crew or company officials.
- Record-Keeping Requirements: Ships are required to maintain an Oil Record Book, where all operations involving oil, including bilge water handling, are meticulously recorded. These records are subject to inspection by port state control officers.
- Regional and National Laws: Beyond MARPOL, many countries and regions have their own laws and regulations concerning marine pollution, which can be more stringent than international standards.
Despite these regulations, enforcement challenges persist, primarily due to the vastness of the oceans and the limitations in monitoring ship activities at sea.
How to Prevent Bilge Dumping
Preventing bilge dumping requires a combination of technological, operational, and educational approaches:
- Advanced Bilge Water Treatment Systems: Modern ships have sophisticated systems that can effectively separate oil from bilge water, reducing the likelihood of illegal discharge.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Ensuring that bilge water treatment systems are functioning correctly and that ships comply with regulations through regular inspections can significantly reduce illegal discharges.
- Crew Training and Awareness: Educating ship personnel about the environmental impact of bilge dumping and the importance of compliance with regulations is crucial.
- Improved Port Facilities: Providing adequate waste reception facilities at ports can encourage legal disposal of bilge water and reduce the temptation to dump it at sea.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Surveillance: Utilizing satellite technology and other monitoring systems can help in detecting illegal discharges and enforcing regulations.
Of course, there are more ways to prevent bilge dumping, but that was just a quick recap of some of the better-known solutions.
Global Initiatives and Collaborations

The fight against bilge dumping has seen various global initiatives and collaborations aimed at strengthening enforcement and raising awareness:
- IMO’s Role: The IMO continues to update and enforce international regulations on marine pollution, and works to enhance global compliance.
- Collaborative Enforcement Efforts: Collaborations between flag states, port states, and international organizations are essential for effective enforcement. Joint inspections and shared intelligence can help in identifying and penalizing offenders.
- International Agreements and Protocols: Various international agreements, like the OSPAR Convention (for the North-East Atlantic), play a significant role in preventing marine pollution, including bilge dumping.
- Awareness Campaigns and Training Programs: International bodies and NGOs often conduct awareness campaigns and training programs for both the maritime industry and the public, emphasizing the importance of preventing marine pollution.
These efforts represent a collective commitment to safeguarding our oceans from the adverse effects of bilge dumping, emphasizing the need for a unified approach in addressing this critical environmental challenge.

I’m Thomas, the owner of SustainableWave. Passionately promoting a sustainable planet. With experience in various eco-roles, I’ll share green tips, sustainability hacks, and personal eco-journeys on my blog.






